Abstract
Introduction: The Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Comorbidity Index (HCT-CI) is a validated tool to predict non-relapsed mortality (NRM) and overall survival (OS) in lymphoma patients (pts) treated with high dose therapy and autologous stem cell transplant (HDT-ASCT) (Sorror, Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2015). Despite hesitation to offer elderly pts with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) treatment with HDT-ASCT, retrospective studies suggest they can be effective and safe (Hosing, Ann Oncol 2008; Dahi, Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2014). It is not known what individual comorbidities in HCT-CI are most impactful on outcomes in elderly pts.
Methods: We conducted a single center retrospective study analyzing NHL pts ≥ 60 years who received HDT-ASCT from 2013-2017. Individual HCT-CI, conditioning regimen, histology, Karnofsky performance status (KPS), readmission at 30 and 60 days post HDT-ASCT, time of relapse, and survival data were analyzed. OS was defined as time from HDT-ASCT to death (TFT), with pts alive censored at last follow-up (LFU). Relapse-free survival (RFS) was defined as TFT or relapse, with pts without relapse censored at LFU. NRM was defined as TFT, relapse, or LFU, with pts alive without relapse censored at LFU. For NRM, pts relapsed were censored at relapse. Survival was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method, and survival distributions were compared using log-rank tests. Univariate Cox proportional hazards models were also fit. Categorical variables were compared across readmission using chi-squared tests or Fisher's Exact tests, and numeric variables were compared using ANOVA.
Results: 115 pts ≥ 60 years old underwent HDT-ASCT from 2013-2017 for NHL, with 44% Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, 29% Mantle cell lymphoma, 18% Peripheral T-cell lymphoma, and 9% other. 69% of pts were male, with median age of 66 years and median follow up of 22 months (m). The BEAM conditioning regimen was used in 76% of pts and 92% of pts had a KPS ≥ 80. HCT-CI identified 42% of pts as high risk (score of ≥3 points), 29% of pts as medium risk (score of 1-2 points), and 29% of pts as low risk (score of 0). The most common individual comorbidities were pulmonary (34% moderate/severe), cardiac (26%), and history of diabetes (18%). Seven (6%) pts were obese (BMI ≥35). Fifteen (13%) pts experienced hospital readmission within 30 days of HDT-ASCT.
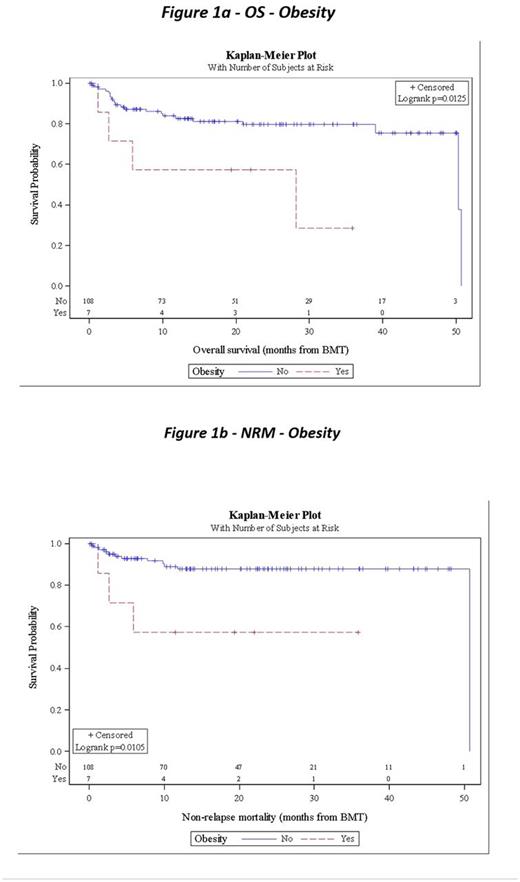
On univariate analysis, obesity was significantly associated with NRM (HR 4.56, 95% CI 1.27-16.35, p=0.011) and OS (HR 3.61, 95% CI 1.23-10.62, p=0.013). Obesity was associated with inferior RFS (HR 2.21, 95% CI 0.78-6.25, p=0.124) worsened RFS but this association was not significant. KPS ≥ 90 (HR = 0.37, 95% CI 0.14-1.00, p=0.049) predicted improved RFS. Psychiatric comorbidity was the only comorbidity significantly associated with 30 day readmission (p=0.009). Pts with high risk HCT-CI compared to medium or low risk had increased 30 day readmission, but this was not statistically significant (19% vs 12% vs 6%, p =0.248). When compared to low-risk HCT-CI, pts with medium risk HCT-CI (HR 3.23, 95% CI 0.65-16.01, p=0.151) and high risk HCT-CI (HR 2.25, 95% CI 0.45-11.16, p=0.320) had increased NRM but neither relationship was statistically significant.
Median OS for the entire cohort was 50.3m from HDT-ASCT, with estimated 12m OS of 82.6% and 24m OS of 79.6% for non-obese pts, and OS of 57.1% at 12 and 24m for obese pts. At 12m, NRM was 14.3% for the entire cohort, 12.2% for non-obese pts, and 42.9% for obese pts. RFS at 12m was 73.3% for the entire cohort.
Discussion: Our findings support prior work suggesting HCT-CI is safe in well-selected elderly pts. The HCT-CI does show a trend toward worse outcomes, although not statistically significant. Readmission rates were associated with psychiatric comorbidity, which may represent pts who are more prone to non-compliance and complications immediately after transplant, although more specific investigation is needed.
Obesity was significantly associated with inferior outcomes (NRM, OS), as well as a trend toward worsened RFS. One possible explanation for this is obese pts are prone to sedentary activity after transplant which may increase NRM. Obesity as defined in HCT-CI is body mass index ≥35, which may not capture the full effect obesity may have on outcome. A limitation was the low number of obese patients in our cohort. Further studies and potential interventions should be considered to evaluate the effect of obesity on HDT-ASCT outcomes.
Nooka: Amgen, Novartis, Spectrum, Adaptive: Consultancy. Kaufman: Amgen, Novartis: Research Funding; Amgen, Roche, BMS, Seattle Genetics, Sutro Biopharma, Pharmacyclics: Consultancy. Waller: AMGEN: Consultancy; Cambium Medical Technologies: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Patents & Royalties; Celldex: Consultancy; PRA: Consultancy; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; National Institutes of Health: Research Funding; Cerus: Equity Ownership; Katz Foundation: Research Funding; Helocyte: Consultancy; Coulter Foundation: Research Funding; Chimerix: Equity Ownership. Flowers: Prime Oncology: Research Funding; National Institutes Of Health: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Millennium/Takeda: Research Funding; Spectrum: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Research Funding; Clinical Care Options: Research Funding; Infinity: Research Funding; OptumRx: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy; Bayer: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy, Research Funding; National Cancer Institute: Research Funding; Onyx: Research Funding; Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group: Research Funding; Research to Practice: Research Funding; Genentech/Roche: Consultancy, Research Funding; Janssen Pharmaceutical: Research Funding; Burroughs Welcome Fund: Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; Educational Concepts: Research Funding; V Foundation: Research Funding. Cohen: Infinity: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; LAM Therapeutics, Inc: Research Funding; Takada: Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bioinvent: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal